Introduction to Quantified Systematic Trading Strategies
Quantified systematic trading strategies leverage mathematical models, statistical methods, and historical market data to make objective, repeatable trading decisions. Unlike discretionary trading, which relies on intuition or market sentiment, these strategies are rules-based and fully testable. The goal is to identify trading opportunities with positive expectancy while minimizing emotional interference.
Originally the domain of hedge funds and institutional investors, quantified systematic trading is now accessible to retail traders and independent quants thanks to automation, algorithmic trading platforms, and historical data availability.
Why Quantified Systematic Trading Works
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Quantitative strategies analyze price, volume, and other market variables to generate signals.
- Backtesting for Reliability: Historical simulation ensures strategies perform under varying market conditions.
- Automation and Efficiency: Computers execute trades faster and more accurately than humans, eliminating emotional errors.
- Portfolio Diversification: Combining multiple strategies reduces risk and stabilizes returns.
- Continuous Optimization: Algorithms can be adjusted over time to adapt to market changes.
Top Quantified Systematic Trading Strategies
Below are some of the most widely-used strategies with proven results.
1. Russell 2000 Rebalancing Strategy
This seasonal strategy trades once a year, targeting the Russell 2000 index during its rebalancing period in June.
Rules:
- Buy on the close of the first trading day after June 23.
- Sell on the close of the first trading day of July.
Backtested Performance:
- Average gain per trade: 1.34%
- Win ratio: 76%
- Max drawdown: 6%
Why it works: Capitalizes on the historical outperformance of small-cap stocks during the rebalancing period.
2. Rubber Band Trading Strategy
A mean-reversion strategy based on short-term price deviations, often applied to indices like the S&P 500.
Rules:
- Calculate 5-day ATR (Average True Range).
- Identify a 5-day high and create a lower band at 2.5× ATR.
- Go long if the price closes below the band; exit when price exceeds previous high.
Backtested Performance:
- Average gain per trade: 0.66%
- Win rate: 77%
- Annual return: 6.4% (invested only 14% of the time)
3. Money Flow Index (MFI) Strategy
MFI combines price and volume to detect overbought and oversold conditions.
Rules:
- Buy when 2-day MFI < 10.
- Exit when the close exceeds yesterday’s high or after 10 trading days.
Backtested Performance on Nasdaq 100 ETF (QQQ):
- Average gain per trade: 0.46%
- Win rate: 70%
- Annual return: 11.1%
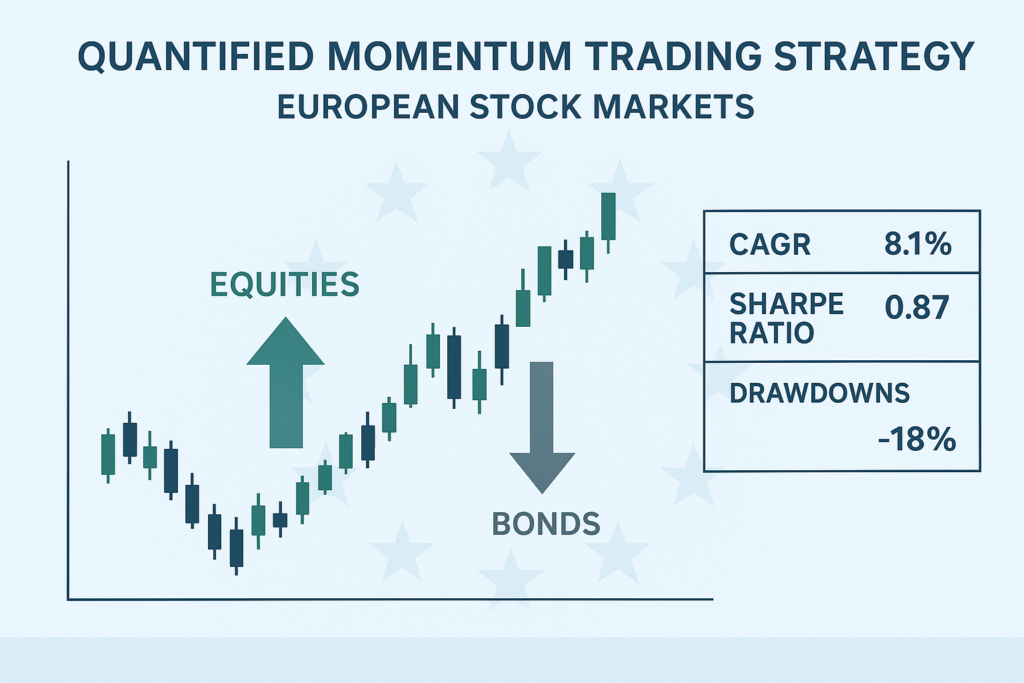
4. Asset Rotation Momentum Strategy
Rotates between stocks, gold, and bonds using momentum indicators.
Rules:
- Select three asset classes: Stocks, Bonds, Gold.
- Invest equally in assets with 3-month SMA > 10-month SMA.
Backtested Performance:
- Average gain per trade: 0.77%
- Annual return: 12%
- Reduced max drawdown compared to Buy & Hold
5. Weekly RSI Strategy
Uses Relative Strength Index (RSI) to exploit mean-reversion in low-volatility assets.
Rules:
- Buy when 2-week RSI < 15.
- Sell when 2-week RSI > 20.
Performance (Consumer Staples ETF XLP):
- Average gain per trade: 1.2%
- Annual returns: 4.2% (invested 11% of the time)
6. Turn-of-the-Month Effect
Trades the last five days of the month and first three of the next month.
Rules:
- Go long on the fifth-last trading day; exit after the third trading day of next month.
Performance:
- Average gain per trade: 0.6%
- Annual return: 7% (with only 33% invested time)
7. Quantitative Volatility Strategy
Focuses on trading volatility across multiple assets using statistical models.
Performance Highlights:
- Average gain per trade (S&P 500 ETF SPY): 1.1%
- Annual return: 6.1% (invested only 8% of the time)
- Max drawdown: 23%
8. Treasury Bonds Long/Short Strategy
Trades long and short positions in government bonds to diversify systematic portfolios.
Backtested Performance:
- Annual return: 9.8% vs. Buy & Hold 4.5%
- Invested 56% of the time
Building a Quantified Systematic Trading Portfolio
Key Principles:
- Diversify Across Strategies: Combine mean-reversion, momentum, volatility, and seasonal strategies.
- Use Multi-Asset Approaches: Trade equities, bonds, and commodities.
- Allocate Risk Wisely: Limit exposure to any single strategy to avoid concentration risk.
- Automate for Consistency: Use trading platforms or APIs to execute strategies without emotion.
Advantages of Quantified Systematic Trading
- Eliminates emotional bias in trading decisions.
- Enables simultaneous execution of multiple strategies.
- Facilitates backtesting, optimization, and performance monitoring.
- Improves risk management through statistical analysis.
Challenges and Considerations
- Requires coding and quantitative skills.
- Strategies may fail under changing market conditions.
- Continuous research is necessary to identify new alpha-generating systems.
- Proper risk management and position sizing are crucial for long-term profitability.
Conclusion
Quantified systematic trading strategies provide a data-driven, disciplined approach to financial markets. By combining multiple strategies, applying rigorous backtesting, and leveraging automation, traders can achieve consistent results while minimizing emotional errors. While mastery requires skill in coding, mathematics, and market analysis, the potential benefits in efficiency, diversification, and risk-adjusted returns make quantified systematic trading a powerful tool for serious traders and aspiring quants alike.